Among the simplest organisms there are many parasites of animals and humans. Below are the parasitic protozoa that cause the most serious and common diseases.
Amoeba dysentery
The dysentery amoeba is similar to the common one, but it is smaller and has shorter and wider rhizomes. At the cyst stage, it enters the human digestive system through the mouth. In the large intestine, the amoeba leaves the cyst and feeds on bacteria without harming humans. In the future, this simplest organism begins to invade the intestinal wall, feed on red blood cells and become a parasite. Ulcers form in the intestine and empty the human body. There is a disease of amoebic dysentery, or amebiasis.
Dysentery amoeba can enter the bloodstream and reach the liver. Here, too, the parasite leads to the formation of purulent ulcers.
Amoebas form cysts and leave the human body with undigested food particles. Mild cysts spread easily. If you don't wash your hands and your food, you can get infected.
Malaria plasmodium
Plasmodia are parasitic protozoa. Some types of plasmodia cause malaria in humans. The malaria mosquito is the carrier of the malaria plasmodia. In the event of an insect bite, the plasmodium enters the host's bloodstream. Together with the blood it reaches the liver, where it feeds, grows and reproduces. After that, many plasmodia get back into the bloodstream and begin to parasitize on erythrocytes, destroying them and releasing their waste products that poison the host. A person develops a fever, he has anemia.
If a malaria patient is bitten again by an Anopheles mosquito, the plasmodia now move from the person to the mosquito. Plasmodium reproduces sexually in the body of a mosquito.
Malaria is widespread in Africa. This is a very dangerous disease. Fight against malaria, including killing malaria mosquitoes.
Trypanosomes
The genus Trypanosomes are parasitic protozoa with flagella (related to Euglena). Their main host is a vertebrate, and insects are usually vectors. Different representatives of trypanosomes cause different diseases in animals and humans. They parasitize mainly in the blood and in the liquor. The best known and most common disease of the trypanosomes is sleeping sickness.
The carrier of sleeping sickness is the tsetse fly. This disease is typical of tropical Africa. Sleeping sickness develops in two stages: The first few weeks of a person are plagued by fever and pain, after a month or more drowsiness, sleep and coordination disorders and a change in consciousness occur. The disease is easier to treat in the first stage.
Giardia
Giardia is a genus of parasitic flagellate protozoa. Darmlammlia causes giardiasis in humans and animals, in which the parasite lives in the small intestine.
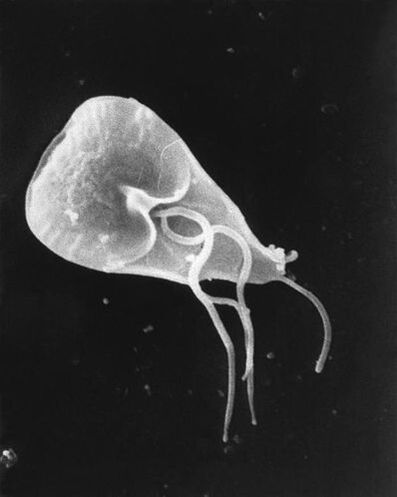
A person becomes infected with giardiasis by ingesting unwashed foods that contain giardia cysts. Coming out of the cyst, lamblia sticks to the intestine and feeds on digested food.
Leishmania
Leishmania is another genus of parasitic protozoa. They cause leishmaniasis in humans and many other animals. The vectors are mosquitos.
There are several types of leishmaniasis that are associated with damage to various tissues in the body. One of these is Pendinsky ulcer skin disease.
Coccidia
Coccidia parasitize many animals, including worms, arthropods, and fish. They cause coccidiosis diseases that cause serious damage to livestock and fish farming.
Coccidia settle in the form of spores that contain parasite cells.
The genus Toxoplasma belongs to the coccidia. Their representatives cause such a widespread disease as toxoplasmosis in humans. A person becomes infected through pets or poorly cooked meat. Toxoplasma affects many organs, including the nervous system.





























